Количество страниц: 4 с.
Gavrilyeva, G. A. Measurements of the mesosphere temperature by two molecular emissions in Yakutsk (62°N, 129,5°E) / G. A. Gavrilyeva // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 198-201.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Ammosov, P. P. Observations of short-term waves with an all sky camera in the infrared oh brightness over Yakutsk / P. P. Ammosov, G. A. Gavrilyeva // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 -28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 179-181.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Moiseyev, A. V. Peculiarities of traveling convection vortices propagation: comparison with sudden geomagnetic impulse / A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, A. Du // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 32nd annual seminar, Apatity, 3 – 6 March 2009. – 2010. – P. 75-78.
Количество страниц: 1 с.
Makarov, G. A. Propagation velocities of geomagnetic sudden impulses caused by sharp changes jf solar wind dinamic pressure at high latitudes / G. A. Makarov, V. Moiseev, and S. I. Solovyev // The First S-Ramp Conference, October 2-6, 2000: Sapporo, Japan. – Sapporo, 2000. – P. 122.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
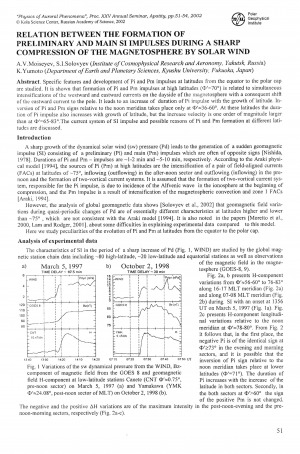
Moiseyev, A. V. Relation between the formation of preliminary and main SI impulses during a sharp compression of the magnetosphere by solar wind / A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, K. Yumoto // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 25th annual seminar, Apatity, 26 February – 1 March 2002. – 2002. – P. 51-54.
Количество страниц: 2 с.
- Математика. Естественные науки > Астрономия. Астрофизика. Исследование космического пространства. Геодезия,
- Математика. Естественные науки > Геология. Геологические и геофизические науки,
- НАУКА ЯКУТИИ > МАТЕМАТИКА. ЕСТЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАУКИ > Астрономия. Астрофизика. Исследование космического пространства. Геодезия,
- НАУКА ЯКУТИИ > МАТЕМАТИКА. ЕСТЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАУКИ > Геология. Геологические и геофизические науки.
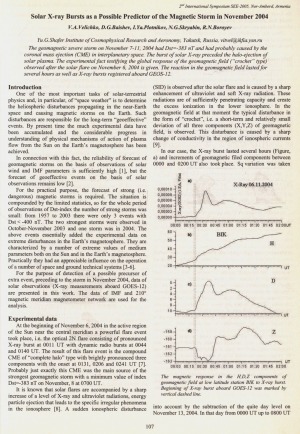
Solar X-ray Bursts as a Possible Predictor of the Magnetic Storm in November 2004 / V. A. Velichko, D. G. Baishev, I. Ya. Plotnikov, N. G. Skryabin, R. N. Boroev // Solar Extreme Events Fundamental Science and Applied Aspects Nor-Amberd, Armenia 26-30 September 2005 : proceedings of the Second International Symposium / edited by A. Chilingarian and G. Karapetyan. − Erevan : Cosmic Ray Division, Alikhanyan Physics Institute, 2006. − P. 107-108.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Splitting of auroral electrojets: ground-based and satellite data / D. G. Baishev, V. A. Velichko, E. E. Antonova, L. I. Gromova, M. V. Stepanova, R. A. Kovrazhkin, J. M. Bosqued // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 9-11.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
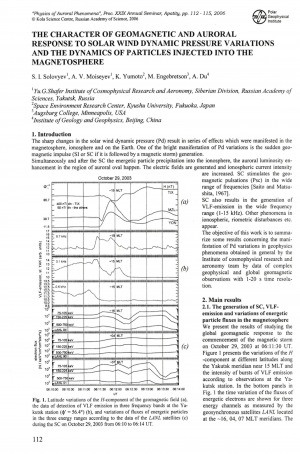
The character of geomagnetic and auroral response to solar wind dynamic pressure variation and the dynamics of particles injected into the magnetosphere / S. I. Solovyev, A. V. Moiseyev, K. Yumoto, M. Engebretson, A. Du // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 29th annual seminar, Apatity, 27 February – 3 March 2006. – 2007. – P. 112-115.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Sokolov, V. D. The dynamics of auroral absorption parameters in the 22nd solar activity cycle / V. D. Sokolov, S. N. Samsonov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 95-97.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Северо-Восток Сибири известен как регион c важными находками мамонтовой фауны и стоянок древних людей последнего ледникового периода, сохраненных в вечной мерзлоте. Минусовые термические условия содействуют сохранению уникальных палеонтологических, палеоботанических и органических археологических материалов, краткосрочно вымытых на поверхность из первичных криолитических геологических слоев древних речных долин эпохи плейстоцена. Проведенные работы в бассейне верхнего и среднего течения реки Колыма в пределах Республики Саха (Якутия) в 2013–2018 гг. принесли новые, подтвержденные радиоуглеродными датами свидетельства обитания человека эпохи палеолита в этом регионе более чем 44 тыс. л. н. Данные полевых исследований позволяют провести реконструкцию природных условий последних десятков тысяч лет и моделирование биологической и культурной адаптации человека к экстремальным условиям последнего интергляциала и гляциала в поясах современной лесотундры.
The mid-last glacial habitats of the palaeolithic peopling of the Kolyma basin, Nortn-East Yakutia=Следы обитания человека эпохи палеолита в интергляциале бассейна Колымы, северо-восток Якутии / J. Chlachula, M. Yu. Cheprasov, T. F. Obada, S. E. Grigoriev // V Северный археологический конгресс, 11-14 декабря 2019, Ханты-Мансийск : тезисы докладов. – Екатеринбург ; Ханты-Мансийск : Альфа-Принт, 2019. – С. 58-60.