Место работы автора, адрес/электронная почта: Институт космофизических исследований и аэрономии им. Ю. Г. Шафера СО РАН ; 677980, г. Якутск, пр-т. Ленина, 31 ; e-mail: moiseyev@ikfia.ysn.ru ; https://ikfia.ysn.ru
Ученая степень, ученое звание: канд. физ.-мат. наук
Область научных интересов: Геофизика, геомагнетизм и высокие слои атмосферы, космические исследования
ID Автора: SPIN-код: 9600-5737, РИНЦ AuthorID: 40463
Деятельность: С 1999 г. работает в Институте космофизических исследований и аэрономии им. Ю. Г. Шафера СО РАН.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
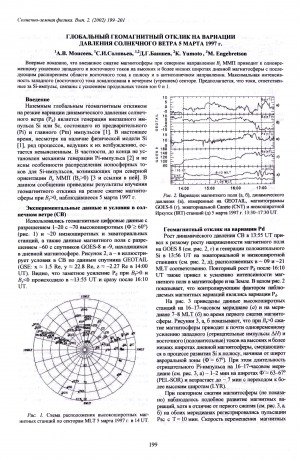
Глобальный геомагнитный отклик на вариации давления солнечного ветра 5 марта 1997 г. / А. В. Моисеев, С. И. Соловьев, Д. Г. Баишев, K. Yumoto, M. Engebretson // Солнечно-земная физика = Solar-Terrestrial Physics. – 2002, вып. 2 (115) : Труды Всероссийской конференции по физике солнечно-земных связей, Иркутск, 24-29 сентября 2001 г. – С. 199-201.
Количество страниц: 2 с.
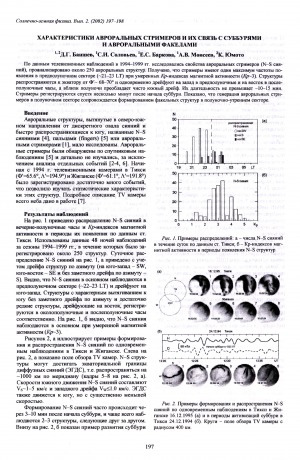
Характеристики авроральных стримеров и их связь с суббурями и авроральными факелами / Д. Г. Баишев, С. И. Соловьев, Е. С. Баркова, А. В. Моисеев, К. Юмото // Солнечно-земная физика = Solar-Terrestrial Physics. – 2002, вып. 2 (115) : Труды Всероссийской конференции по физике солнечно-земных связей, Иркутск, 24-29 сентября 2001 г. – С. 197-198.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
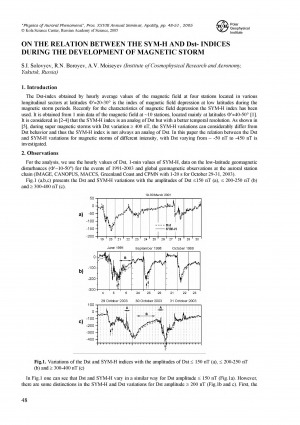
Solovyev, S. I. On the relation between the SYM-H and Dst- indices during the development of magnetic storm / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroyev, A. V. Moiseyev // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 28 th annual seminar, 1-4 March 2005. – 2005. – P. 48-51.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
International project MAGDAS and a contribution of Russian scientific research institutes to this project are briefly discussed. First results of geomagnetic observations using a chain of MAGDAS-9 magnetometers in the territory of Yakutia are presented.
Международный проект MAGDAS: первые результаты геомагнитных наблюдений на территории Якутии / Д. Г. Баишев, А. В. Моисеев, Р. Н. Бороев, Г. А. Макаров, И. Н. Поддельский, А. И. Поддельский, Б. М. Шевцов, K. Yumoto // Наука и образование. – 2013. – N 1 (69). – С. 7-10.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Moiseyev, A. V. Peculiarities of traveling convection vortices propagation: comparison with sudden geomagnetic impulse / A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, A. Du // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 32nd annual seminar, Apatity, 3 – 6 March 2009. – 2010. – P. 75-78.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
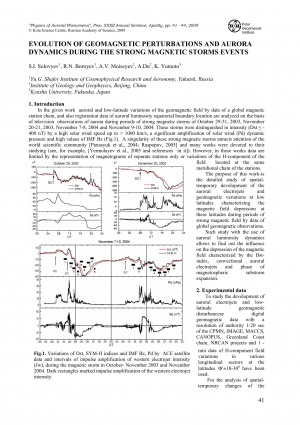
Evolution of geomagnetic perturbations and aurora dynamics during the strong magnetic storms events / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroev, A. V. Moiseyev, A. Du, K. Yumoto // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 32nd annual seminar, Apatity, 3 – 6 March 2009. – 2010. – P. 41-44.
Количество страниц: 6 с.
Geomagnetic signatures of current wedge produced by fast flows in a plasma sheet / Jin-Bin Cao, Chunxiao Yan, Malcolm Dunlop, Henri Reme, Iannis Dandouras, Tielong Zhang, Dongmei Yang, Alexey Moiseyev, Stepan I. Solovyev, Z. Q. Wang, A. Leonoviche, N. Zolotukhina, and V. Mishin // Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. – 1978. – 2010 (August), vol. 115, N 8. – P. A08205.
Количество страниц: 14 с.
Evolution of negative SI-induced ionospheric flows observed by SuperDARN King Salmon HF radar / T. Hori, A. Shinbori, N. Nishitani, T. Kikuchi, S. Fujita, T. Nagatsuma, O. Troshichev, K. Yumoto, A. Moiseyev, and K. Seki // Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. – 1978. – 2012 (December), vol. 117, N 12. – P. A12223.
DOI: 10.1029/2012JA018093
Количество страниц: 4 с.
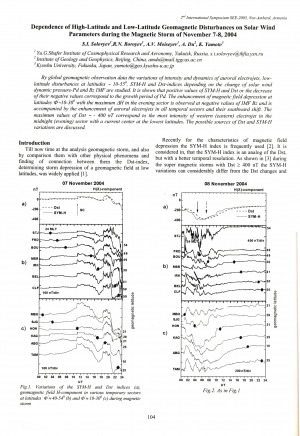
Dependence of High-Latitude and Low-Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances on Solar Wind Parameters during the Magnetic Storm of November 7-8, 2004 / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroyev, A. V. Moiseyev, A. Du, K. Yumoto // Solar Extreme Events Fundamental Science and Applied Aspects Nor-Amberd, Armenia 26-30 September 2005 : proceedings of the Second International Symposium / edited by A. Chilingarian and G. Karapetyan. − Erevan : Cosmic Ray Division, Alikhanyan Physics Institute, 2006. − P. 104-106.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
High-latitude peculiarities of the geomagnetic SI impulse propagation meridional velocity during sharp decrease of solar wind density / G. A. Makarov, D. G. Baishev, A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, V. A. Pilipenko, M. J. Engebretson, K. Yumoto // Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Substorms : 16-20 May 2000 Congress Centre of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia. − Noordwijk, Netherlands : European Space Agency, 2000. − P. 523-526.