Количество страниц: 4 с.
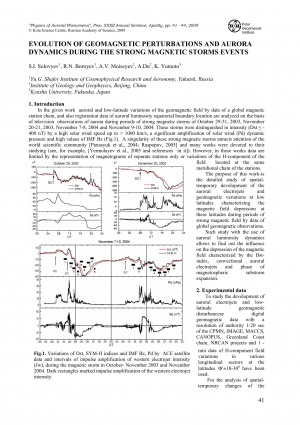
Evolution of geomagnetic perturbations and aurora dynamics during the strong magnetic storms events / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroev, A. V. Moiseyev, A. Du, K. Yumoto // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 32nd annual seminar, Apatity, 3 – 6 March 2009. – 2010. – P. 41-44.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
High-latitude peculiarities of the geomagnetic SI impulse propagation meridional velocity during sharp decrease of solar wind density / G. A. Makarov, D. G. Baishev, A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, V. A. Pilipenko, M. J. Engebretson, K. Yumoto // Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Substorms : 16-20 May 2000 Congress Centre of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia. − Noordwijk, Netherlands : European Space Agency, 2000. − P. 523-526.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
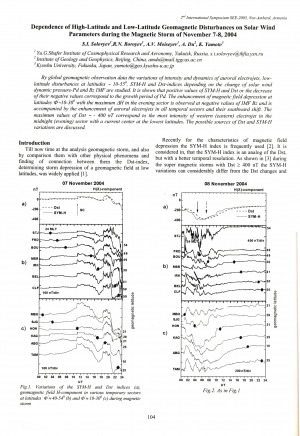
Dependence of High-Latitude and Low-Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances on Solar Wind Parameters during the Magnetic Storm of November 7-8, 2004 / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroyev, A. V. Moiseyev, A. Du, K. Yumoto // Solar Extreme Events Fundamental Science and Applied Aspects Nor-Amberd, Armenia 26-30 September 2005 : proceedings of the Second International Symposium / edited by A. Chilingarian and G. Karapetyan. − Erevan : Cosmic Ray Division, Alikhanyan Physics Institute, 2006. − P. 104-106.
Количество страниц: 2 с.
Characteristics of negative sudden geomagnetic impulses: Comparison with the sudden geomagnetic impulse caused by the growth of the solar wind dynamic pressure : [тезисы докладов] / A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, K. Yumoto, M. Engebretson // Physics of auroral phenomena : 30th annual seminar, 27 February – 2 March 2007 : abstracts. – 2007. – P. 34-35.
Количество страниц: 2 с.
Dependence of distribution of the sudden impulse ionospheric currents on IMF orientation during growth periods of the solar wind dynamic pressure : [тезисы докладов] / A. V. Moiseyev, S. I. Solovyev, K. Yumoto, M. Engebretson // Physics of auroral phenomena : 26th annual seminar, 25-28 February 2003 : abstacts. – 2003. – P. 24.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
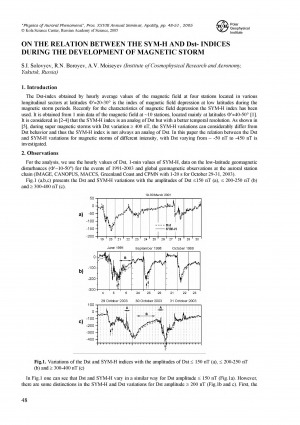
Solovyev, S. I. On the relation between the SYM-H and Dst- indices during the development of magnetic storm / S. I. Solovyev, R. N. Boroyev, A. V. Moiseyev // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 28 th annual seminar, 1-4 March 2005. – 2005. – P. 48-51.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Formation of polarization jet during injection of ions into the inner magnetosphere / V. L. Khalipov, Yu. I. Galperin, A. E. Stepanov, E. D. Bondar // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 25th annual seminar, Apatity, 26 February – 1 March 2002. – 2002. – P. 43-46.
DOI: 10.1016/S0273-1177(03)00016-4
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Skryabin, N. G. Influence of Jupiter on cosmic ray intensity variations / N. G. Skryabin, S. N. Samsonov, I. Ya. Plotnikov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 25th annual seminar, Apatity, 26 February – 1 March 2002. – 2002. – P. 137-139.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Splitting of auroral electrojets: ground-based and satellite data / D. G. Baishev, V. A. Velichko, E. E. Antonova, L. I. Gromova, M. V. Stepanova, R. A. Kovrazhkin, J. M. Bosqued // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 9-11.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
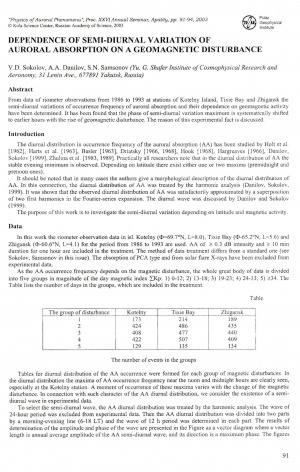
Sokolov, V. D. Dependence of semi-diurnal variation of auroral absorption on a geomagnetic disturbance / V. D. Sokolov, A. A. Danilov, S. N. Samsonov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 91-94.